Black holes:
As it turns out black holes as theoretical objects are a consequence of some basic physics that we just explored (energy). We will start there and move forward.
Escape Velocity:
The faster something is thrown up in the air the farther away it goes before it falls back to earth -- no surprises there. Probably many of us experimented with this idea when we were kids trying to see how far we could get a ball to go. One can certainly imagine getting an object going fast enough that it would leave the earth forever or at least make it into orbit. For an object, like a ball, that has no internal means of propulsion we can actually calculate what that speed is from our understanding of gravity.
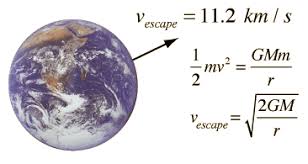
Given that light is the fastest thing we know of we can calculate the radius of an object for whom the escape velocity is the speed of light. You may be aware that we usually indicate the speed of light with the symbol c where c = 3 108 m/s which is very fast. What this means is that if an object of particular mass gets small than some radius even light will not be able to escape. That radius is given by this expression (algebra from the one above).

This is known as the Schwarzschild radius and is the same as the radius of the event horizon.
This is all well and good. It suggests that there could be such a thing as an object from which light can not escape (that would make it black!) but how would it form and how could we detect it? These were the original questions related to black holes and they are the same ones we now confront with white holes. Before we go off to talk about white holes a few comments about the search for black holes.
Black Holes:
We've been thinking about black holes for a long time and have various models for what we expect to happen around and near black holes. Those models suggest certain types of radiation are expected to be released as material falls into the black hole. This is what we call the signature of a black hole. Eventually, as we developed new instruments and better telescopes, we started to see objects in the universe that showed the predicted signature of a black hole. This is why we say that we believe that there is a super massive black hole at the center of our galaxy.
Here is a presentation from Veritasium that may help you understand what the image is telling us.
Since he references his presentation on spinning black holes I include it here.
...and then there's the question of 'evaporation' of black holes. I don't know anything about this and I can barely understand this article but here it is in case you're interested.
Ethan Siegel again -- Evaporation of Black Holes: A consequence of the ideas in this article is that smaller black holes actually evaporate faster than big one. That's why we weren't supposed to worry if CERN created some microscopic black holes as they were looking for the Higgs Boson. A lot of trust involved there......
