1) In electronic equipment wires which carry equal and opposite currents are often twisted together to reduce magnetic field effects. How does this work to reduce the magnetic field near the wire?
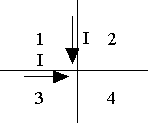
2) Two fixed wires cross perpendicularly to one another as shown.Equal currents flow in each wire. In which region(s) will there be no net magnetic field? (1,4) |
|
3) A square loop of wire is carrying a current I and has sides of length a. What is the B field at the center of the square? You will need to find the formula for the magnetic field of a non-infinite piece of wire.
![]()
4) Parallel power lines carry 100 amps in the same direction. If the power lines are separated by 3 m what is the force each wire exerts on 10 m of the other?
6E-3 N
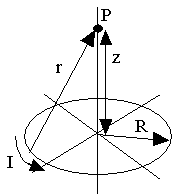
5) Use the Biot-Savart Law to find the B field at point P in the drawing to the right. You should get along the z axis. |
|
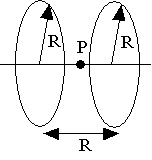
6) Two coils of N turns facing each other with the same current in each coils is known as a Helmholtz Coil. Use the result of the previous problem to find the B field midway between the two coils.
|
|
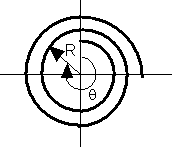
7) Suppose you wind a wire into a spiral whose radius is 1.e-4*θ meters where θ is the angular position of the wire in radians. Run a current of 10 A through the wire. What is the B field at the center of such a spiral where the inner radius is 5 cm and the outer radius is 15 cm?
|
|
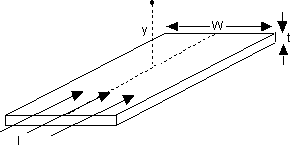
8) Here’s an interesting one with double credit if you get it right. Consider a long (infinite) flat bar of metal of width W and thickness t which is carrying a total current I in the direction indicated. What is the total magnetic field a distance y above the center of the bar? Think of this as a bunch of wires laying next to each other each contributing to the magnetic field. |
|